Understanding the Importance of SMA Male Connectors in Modern Technology Systems
In contemporary technological ecosystems, the significance of the SMA male connector cannot be overstated. As industries increasingly gravitate towards higher frequency communications and compact design in devices, the SMA male connector has emerged as a pivotal component due to its reliability and performance. According to a report by the global market research firm MarketsandMarkets, the RF connectors market is projected to reach USD 3.02 billion by 2024, with a substantial contribution attributed to the growth in wireless communication technologies and advancements in telecommunications infrastructure. Notably, SMA connectors offer superior mechanical strength and minimal signal loss, making them essential for applications ranging from microwave systems to telecommunications and automotive technologies. As the demand for efficient and effective connectivity solutions escalates, understanding the role of SMA male connectors becomes vital for engineers and technologists striving to optimize system performance in various modern technology initiatives.
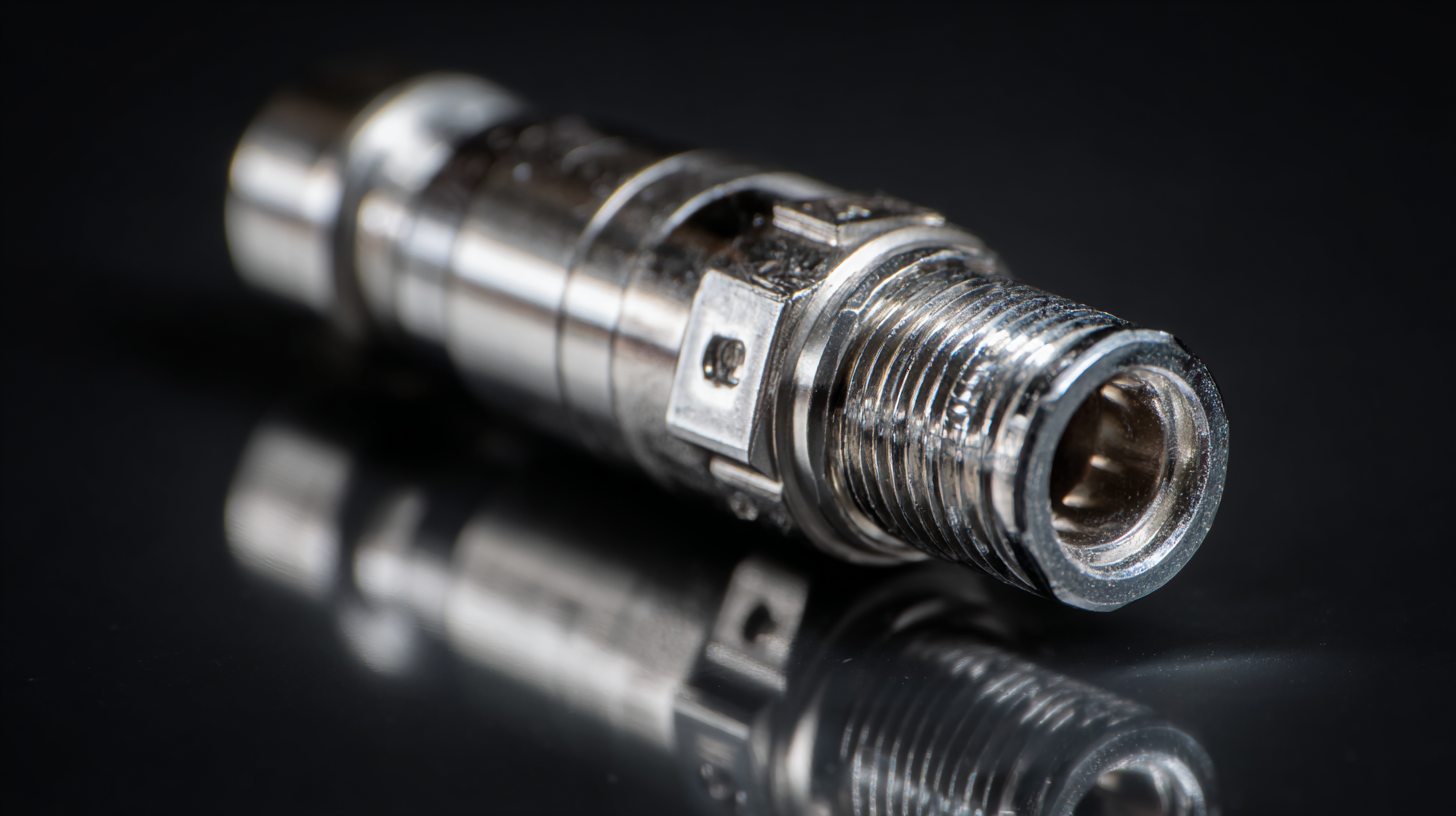

The Evolution of SMA Male Connectors in Telecommunications: A Historical Perspective
The evolution of SMA Male Connectors has played a crucial role in the advancement of telecommunications systems over the past several decades. Originally developed in the 1960s, these connectors facilitated the integration of high-frequency technology, marking a significant leap in communication effectiveness. By allowing interconnectivity of various devices, SMA connectors have optimally addressed the increasing demands for data transmission and signal integrity, making them indispensable in modern technology systems.
As societies evolved during the Holocene, so did the need for more sophisticated communication tools. The ongoing shift towards digitalization and the Internet of Things (IoT) has heightened the necessity for reliable connectors. According to industry reports, the global RF connector market is projected to reach $6.29 billion by 2025, driven mainly by advancements in cellular networks and aerospace technologies. This emphasizes the importance of robust connector systems, such as SMA Male Connectors, which provide excellent performance in terms of frequency stability and resistance to environmental factors. The continuous innovation in connector technology mirrors the broader societal trend of increasing administrative layers and information processing capabilities, underscoring their vital role in sustaining modern communication infrastructures.
Understanding the Importance of SMA Male Connectors in Modern Technology Systems - The Evolution of SMA Male Connectors in Telecommunications: A Historical Perspective
| Year | Technological Development | SMA Connector Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1960s | Introduction of coaxial cable technology | First SMA connector designs | Telecommunications and broadcasting |
| 1980s | Widespread adoption of Rx/Tx systems | Improved durability and performance | Satellite communications |
| 1990s | Growth of wireless technology | Compact design for RF applications | Mobile phones and wireless networks |
| 2000s | Advancements in 4G technology | Enhanced frequency range | High-speed internet services |
| 2010s | Emergence of IoT devices | Miniature SMA connectors | Smart home technology |
| 2020s | Expansion of 5G technology | Ultra-low loss connectors | Next-gen telecommunications |
Key Specifications of SMA Male Connectors: Performance Metrics and Standards
SMA male connectors play a critical role in modern technology systems, particularly in applications involving RF (radio frequency) signals. Their performance metrics are key to ensuring efficient signal transmission and minimizing loss. These connectors typically feature a threaded coupling mechanism, which provides excellent durability and reliability. It's essential to understand specifications such as frequency range, VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio), and insertion loss when selecting SMA connectors for your system. A standard SMA connector can operate effectively up to 18 GHz, making it suitable for various applications including telecommunications, aerospace, and automotive industries.
**Tip:** When choosing SMA male connectors, consider their maximum power rating to prevent overheating and signal distortion. Over time, connectors can wear out, so regularly checking their integrity can enhance system performance.
Another important specification is the material used in the construction of SMA connectors. Common materials include brass, stainless steel, and copper. These materials affect the connector's performance in terms of corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. Additionally, paying attention to the connector's impedance—commonly 50 ohms or 75 ohms—ensures compatibility with your equipment, reducing signal reflections and improving overall data integrity.
**Tip:** Always match the impedance of your SMA connectors with the associated cables to optimize performance and minimize loss.
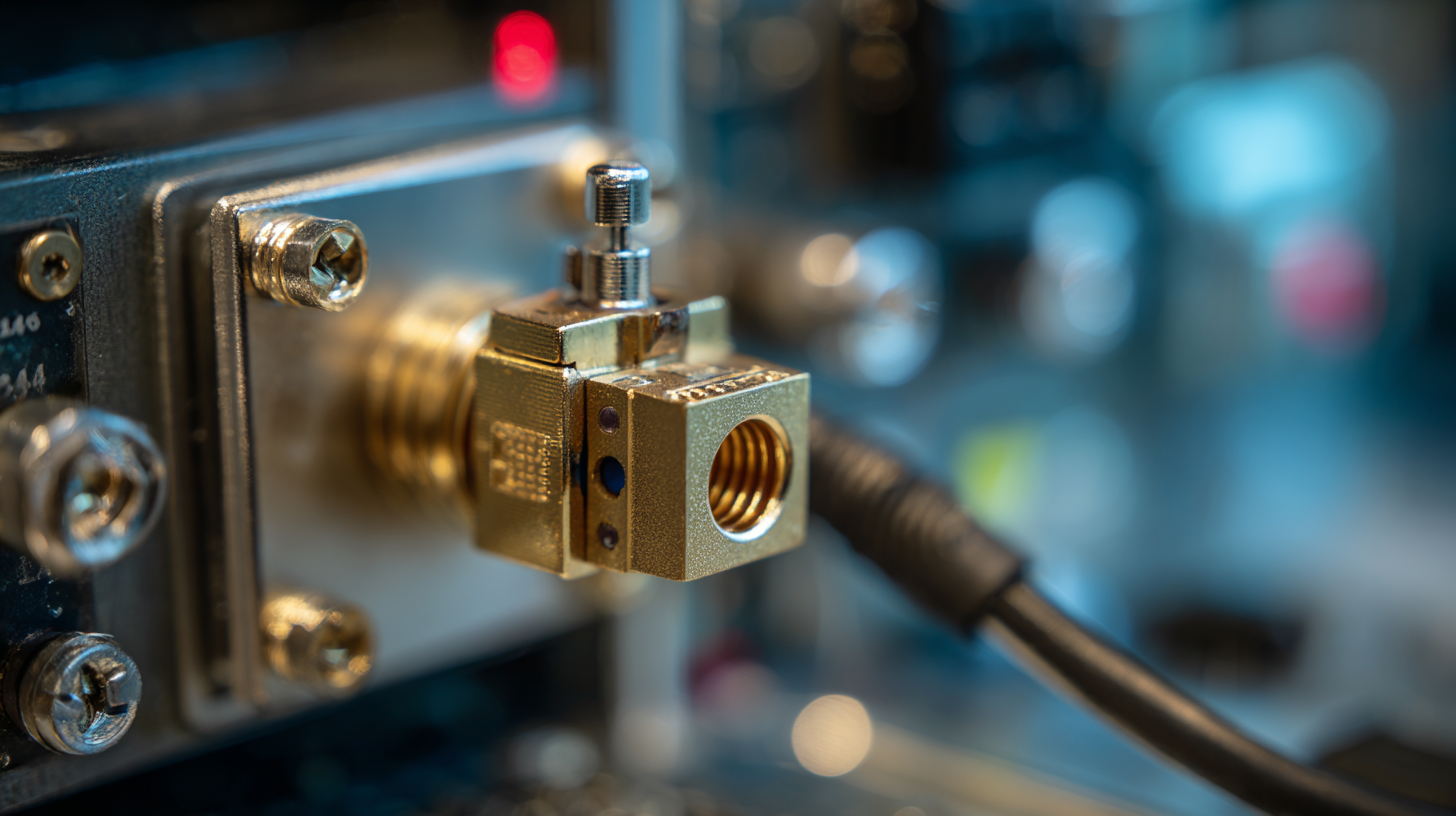

Industry Applications of SMA Male Connectors: Connectivity Solutions in Modern Technology
SMA male connectors have become a critical component in various modern technology systems, serving as reliable connectivity solutions across multiple industries. Their robust design and ability to maintain mechanical stability under varying conditions make them ideal for applications in telecommunications, aerospace, and medical devices. In telecommunications, SMA connectors facilitate high-frequency signal transmission, essential for efficient communications systems. Their precision and durability ensure that data integrity is upheld, even in challenging environments.
In the aerospace sector, SMA male connectors are utilized in satellite communication and radar systems. Their lightweight design coupled with excellent electrical performance allows for the development of advanced avionics that require reliable signals over long distances. Additionally, in the medical field, these connectors are crucial in devices where accuracy is paramount, such as in imaging systems and diagnostic equipment. The versatility and effectiveness of SMA male connectors highlight their importance in enhancing connectivity solutions that drive innovation across various technological landscapes.
Comparative Analysis: SMA Male Connectors vs. Alternative Connector Types
 SMA male connectors have become a staple in modern technology systems, primarily due to their efficiency and reliability in high-frequency applications. A comparative analysis reveals that while SMA connectors excel in RF performance, they hold notable advantages over alternatives such as N-type and BNC connectors. According to a recent industry report by Smiths Connectors, SMA connectors maintain a lower insertion loss and better return loss characteristics, which makes them ideal for telecommunication and aerospace applications, where signal integrity is critical.
SMA male connectors have become a staple in modern technology systems, primarily due to their efficiency and reliability in high-frequency applications. A comparative analysis reveals that while SMA connectors excel in RF performance, they hold notable advantages over alternatives such as N-type and BNC connectors. According to a recent industry report by Smiths Connectors, SMA connectors maintain a lower insertion loss and better return loss characteristics, which makes them ideal for telecommunication and aerospace applications, where signal integrity is critical.
In addition, SMA connectors are smaller and lighter than many alternatives, making them more suitable for compact electronic designs. With a frequency range usually up to 18 GHz and beyond, they can facilitate a wider bandwidth, which is increasingly essential in advancements like 5G technology. Depending on the application, selecting the right connector can significantly impact performance; thus, understanding these differences is crucial for engineers and designers.
Tips: When selecting a connector, consider the operating environment. For high-vibration applications, using SMA connectors can provide better durability due to their secure connection. Moreover, always check the frequency requirements of your application, as using a connector that exceeds your required bandwidth can lead to unnecessary costs without performance benefits.
Future Trends: Innovations in SMA Male Connectors for 5G and Beyond
The evolving landscape of connectivity is ushering in a new era as technologies such as 5G and artificial intelligence converge to create unprecedented opportunities for businesses. As the fifth generation of mobile networks, 5G promises ultra-fast data transfer rates, low latency, and the capacity to connect a myriad of devices simultaneously. According to industry reports, the global 5G technology market is projected to exceed $700 billion by 2027, highlighting the urgency for advancements in supporting infrastructure, including SMA male connectors. These connectors play a crucial role in ensuring reliable and efficient connections within 5G networks, facilitating seamless data transmission necessary for applications ranging from smart cities to autonomous vehicles.
As we look ahead, the innovations in SMA male connectors will significantly influence the trajectory of 5G and beyond. The integration of edge computing, powered by 5G technology, allows for immediate data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and improving service quality. For instance, as telecom companies enhance their offerings, SMA connectors must evolve to handle increased bandwidth and support the anticipated rollout of 6G networks. Industry experts predict that by 2030, 6G networks will be capable of delivering speeds up to 1 Tbps, emphasizing the need for robust connector technologies that can support this demand for higher performance and efficiency.
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Right SMA Male Connector for Your Project
-

What You Need to Know About SMA Male Connectors for Your Next Project
-

What is a Cable Wire Harness and How Does It Power Modern Innovations?
-

Innovative Applications of Molded Cable Assemblies Across Various Industries
-

5 Essential Reasons Your Business Needs a Reliable Cable Harness Supplier
-

How to Optimize Your Electrical Harness Assembly for Maximum Efficiency