Top Wire Harness Design Techniques for Optimal Performance?
Wire harness design is critical in ensuring optimal performance across various industries. Industry expert Mark Johnson once stated, “A well-designed wire harness is the backbone of reliable electronics.” This reinforces the importance of effective wire harness design in enhancing connectivity and functionality.
In today's fast-paced technological landscape, wire harness design demands meticulous attention. Manufacturers must consider factors such as materials, layout, and environmental conditions. However, many overlook the significance of testing and quality control in this process. There are cases of failures that could have been prevented with better planning.
Moreover, the industry often grapples with standardization issues. Different projects require unique specifications, leading to inconsistencies. This presents challenges for designers aiming to deliver optimal solutions. Achieving perfection in wire harness design is a continuous learning journey. Embracing new techniques and reflecting on past mistakes is essential for growth.
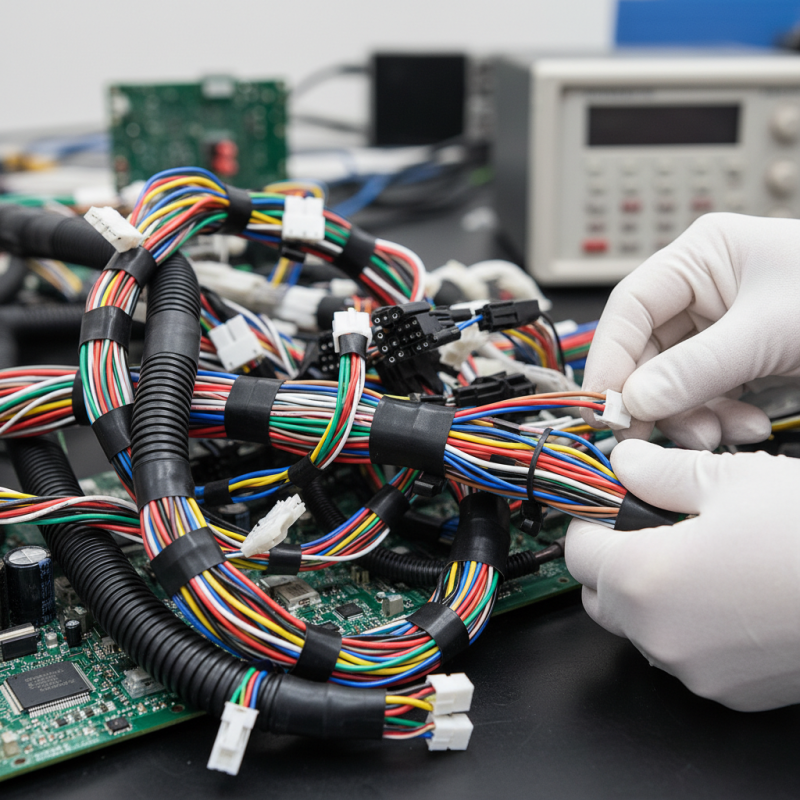
Essential Principles of Wire Harness Design for Optimal Performance
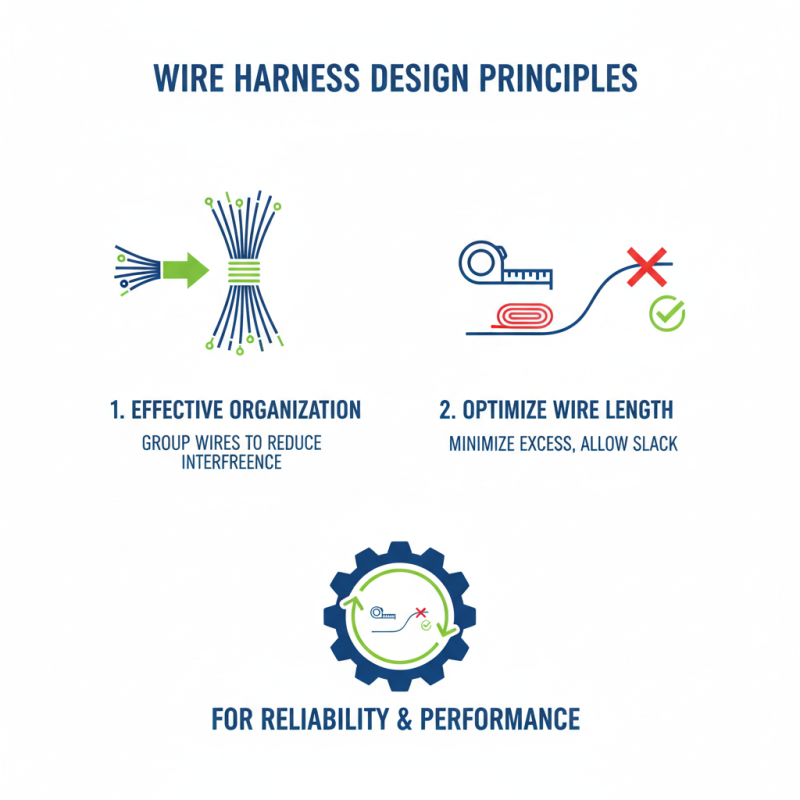
When designing wire harnesses, several principles are crucial for achieving optimal performance. One key element is effective organization. Properly grouping wires reduces the chances of interference. It’s essential to consider wire lengths carefully. Overly long wires can create tension and potential failure points. Aim for a design that minimizes excess length while maintaining necessary slack.
Another vital aspect is shielding and insulation. Adequate protection against electromagnetic interference can enhance performance. Selecting the right materials for insulation can prevent issues. However, many overlook the trade-offs between flexibility and protection. A balance must always be struck. Testing different configurations can provide insights into performance limitations that may not be immediately apparent.
Moreover, heat management is often an afterthought. Harness designs need to account for temperature fluctuations. Ignoring this can lead to degradation over time. Using heat-resistant materials is one way to mitigate such risks. Still, it’s essential to periodically evaluate the impact of high temperatures on your design choices. Continuous improvement and reflection can lead to breakthroughs in design efficiency.
Choosing the Right Materials for Efficient Wire Harness Construction
Choosing the right materials is crucial for efficient wire harness construction. The material affects durability, flexibility, and performance. Common options include PVC, Teflon, and silicone. PVC is cost-effective, but not as heat-resistant. Teflon stands out for high-temperature environments. Silicon offers great flexibility but may lack some structural integrity.
When selecting materials, consider the environment. Harsh conditions can break down lower-quality options. Conducting thorough tests on material samples helps identify potential issues. Don't overlook insulation; it plays a vital role in preventing short circuits.
Tips:
1. Always analyze the electromagnetic interference in your application. Proper shielding can mitigate issues.
2. In high-vibration scenarios, choose materials that maintain their integrity.
3. Regularly review and update your material knowledge to stay informed about advancements.
Improper material choices can lead to disputes and failures. The cost of materials should never compromise quality. Properly evaluating each component of a wire harness is essential for optimal performance.
Top Wire Harness Design Techniques for Optimal Performance
This chart illustrates the effectiveness of different materials used in wire harness construction based on their performance in various categories such as durability, flexibility, and cost.
Innovative Techniques for Reducing Interference in Wire Harnesses
Innovative techniques for reducing interference in wire harnesses are increasingly essential in today's electronics. Interference can lead to significant performance issues. A study by Datasheet World indicates that over 30% of wire harness failures stem from electromagnetic interference (EMI). This statistic highlights the need for robust design techniques to ensure system reliability.
One method involves using twisted pairs of wires. This technique helps cancel out electromagnetic interference. Additionally, proper shielding can minimize unwanted signals. According to the IPC-2221 standard, careful consideration of grounding methods can also enhance performance. For example, ground planes can provide a stable reference for signals, which can improve overall circuit integrity.
The layout of the wire harness plays a crucial role. Maintaining a consistent spacing between wires is vital. A close proximity can increase crosstalk between adjacent wires. Moreover, effective routing can prevent undesired electromagnetic coupling. These design strategies require careful planning and precise execution. Regular testing and validation are necessary to identify potential improvements and address shortcomings. Each step offers a chance for reflection and optimization in wire harness design.
Top Wire Harness Design Techniques for Optimal Performance
| Technique | Description | Benefits | Interference Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Twisted Pair Wiring | Uses pairs of wires twisted together to cancel electromagnetic interference. | Improves signal integrity and reduces noise. | Medium |
| Shielding | Involves encasing wires in conductive materials to block interference. | Enhanced protection against external noise and disturbances. | High |
| Proper Grounding | Ensures a low-resistance path for electrical currents to ground. | Reduces voltage noise and improves system stability. | Medium |
| Ferrite Beads | Used to suppress high-frequency noise in cables. | Helps in maintaining clarity in signal transmission. | Medium to High |
| Cable Management | Organizes cables to prevent tangling and crosstalk. | Facilitates maintenance and enhances airflow. | Low |
Best Practices for Wire Routing and Layout for Performance Enhancement
Wire routing is critical in harness design. The layout directly affects performance and reliability. One common mistake is overcrowding. If wires are too close, they may interfere with each other. This can lead to signal loss or even failure. A well-planned space can avoid these issues. Aim for organized pathways that allow for airflow.
Bends and twists in wires can also hinder performance. Sharp angles should be avoided as they create stress. Instead, gentle curves are preferred. This allows for better flexibility and durability. Consider how wires will move during operation. Are they secure? Are they prone to chafing? Addressing these questions can prevent future problems.
Another aspect is the choice of materials. Not all wires are created equal. Some may not perform well under certain conditions. The environment should guide material selection. Think about temperature, moisture, and potential exposure to chemicals. Testing different configurations can yield surprising results. Not every design will be perfect. Continuous improvement is key in wire harness design.
Testing and Validation Methods for Wire Harness Performance Optimization
Testing and validation methods are essential for ensuring wire harness performance. Different approaches can reveal critical issues that affect functionality. One key aspect is thermal testing. This measures how the harness reacts to heat. Weak points often emerge under stress. Regular thermal checks can highlight areas needing reinforcement.
Another effective method is vibration testing. This simulates real-world conditions that a harness might face. It helps identify weaknesses in connections or materials. Many designs fail to hold up under vibration. Evaluating harnesses in this way could lead to better reliability in various applications.
Lastly, environmental testing is vital. It examines how harnesses perform in extreme conditions. Humidity, salt spray, and temperature extremes are common tests. However, ensuring each harness meets durability standards can be challenging. Some designs may not perform well in unexpected environments. Reflecting on these tests can improve future designs and enhance overall performance.
Related Posts
-

Revolutionizing Your Production: The Future of Wire Harness Design and Its Impact on Manufacturing Efficiency
-

The Definitive Ultimate Guide to Mastering Wire Harness Assembly for Optimal Performance
-

What is a Cable Wire Harness and How Does It Power Modern Innovations?
-

2026 How to Choose the Right Cable and Harness for Your Needs?
-

Explore Superior Wire Harness Assembly Solutions from Leading Chinese Manufacturers
-

Challenges Faced in Cable Harness Design Efficiency